Impaired Proteasome Function In Alzheimer’s Disease
Citations of this article. Impaired function of UPP results in accumulation of misfolded and ubiquitinated proteins and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative diseases including polyglutamine diseases.
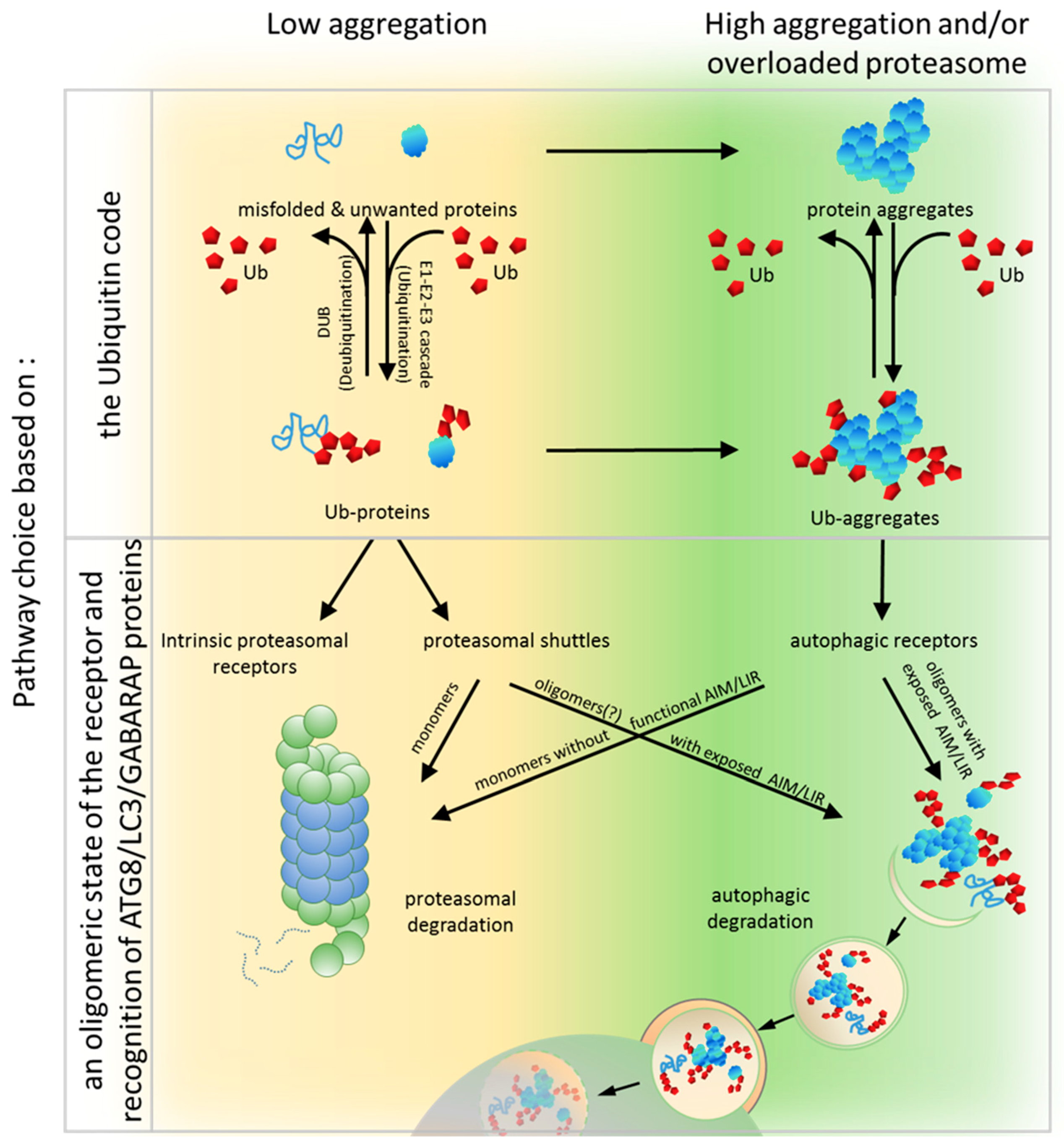
Cells Free Full Text The Roles Of Ubiquitin Binding Protein Shuttles In The Degradative Fate Of Ubiquitinated Proteins In The Ubiquitin Proteasome System And Autophagy Html
Inhibition of proteasome activity is.
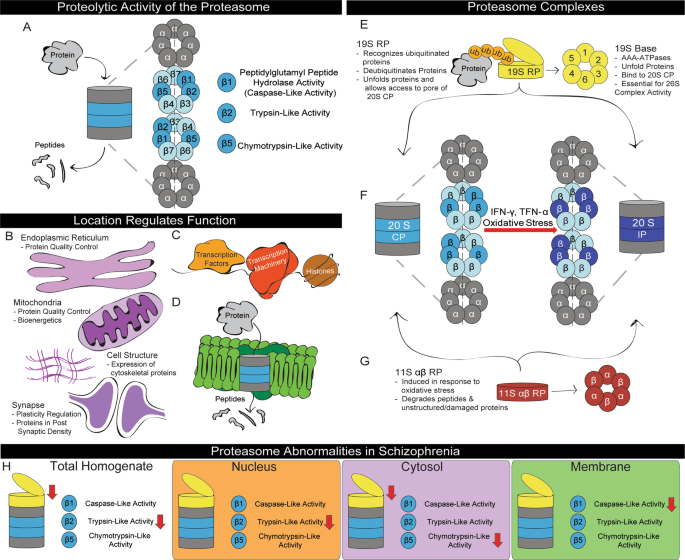
Impaired proteasome function in alzheimer’s disease. Mendeley users who have this article in their library. Recent studies implicate a possible role for proteasome inhibition in neuron degeneration and death that occurs in Alzheimers disease AD. The glymphatic system therefore represents an exciting new target for Alzheimers disease.
An impaired ubiquitin-proteasome system UPS could lead to negative consequences for protein regulation including loss of function. However altered proteasome activity in a neurodegenerative disorder has not been demonstrated. Inhibition of proteasome activity is sufficient to induce neuron degeneration and death.
This system degrades many cellular proteins including beta-catenin a member of the Wnt signaling pathway and a presenilin-1-interacting protein. Alzheimers disease AD is a neurodegenerative disorder affecting numerous people around the world. One such pathway for parenchymal protein clearance the glymphatic system has recently been described Jessen et al 2015.
Impaired proteasome function has been implicated as a primary cause or a secondary consequence in the pathogenesis of many neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimers Parkinsons and. In the present study we analyzed proteasome activity in shortpostmorteminterval autopsied brains from 16 Alzheimers disease AD and nine age and sexmatched controls. Journal of Neurochemistry 2000 751 436-439.
Though Alzheimers disease AD is a syndrome with well-defined clinical and neuropathological manifestations an array of molecular defects underlies its pathology. 24 both of which are believed to contribute to the progression of AD 16. Here we aim to understand the involvement of glymphatic CSF-ISF exchange in tau pathology.
This artice is free to access. Accumulation of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in many neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimers disease AD might result from dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. A role for the ubiquitin proteasome system UPS was suspected in the pathogenesis of AD since the presence of ubiquitin immunoreactiv.
A significant decrease in proteasome activity was observed in the hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus 48 superior and middle temporal gyri 38 and inferior parietal lobule 28 of AD patients compared with controls. Impaired proteasome function in Alzheimers disease Inhibition of proteasome activity is sufficient to induce neuron degeneration and death. Perturbation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system UPS has long been considered an attractive hypothesis to explain the pathogenesis of AD.
However studies on UPS functionality. Molecular chaperones such as heat shock proteins HSPs and FK506-binding proteins FKBPs are highly involved in protein regulation to. First we demonstrate impaired CSF-ISF exchange and AQP4 polarization in a mouse model of tauopathy suggesting that this clearance pathway may have the potential to exacerbate or even induce.
Proteasome activity is inhibited by the application of amyloid βpeptide and exposure to oxidative stress 7. Proteasome activity is inhibited by the application of amyloid b-peptide and exposure to oxidative. A significant decrease in proteasome activity was observed in the hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus 48 superior and middle temporal gyri 38 and inferior parietal lobule 28 of AD.
These new insights into the mechanisms regulating proteasome function and the degradation of misfolded proteins indicate a very promising approach for development of novel drugs to inhibit the progression of Alzheimers Disease AD and other tauopathies. In contrast no significant decrease in proteasome activity. In the present study we analyzed proteasome activity in shortpostmorteminterval autopsied brains from 16 Alzheimers disease AD and nine age and sexmatched controls.
However altered proteasome activity in a neurodegenerative disorder has not been demonstrated. Role of the proteasome in the CNS has not been determined. Another pivotal mechanism for the prevention of misfolded protein accumulation is the utilization of molecular chaperones.
Impaired brain clearance mechanisms that result in the accumulation of aberrant proteins that define Alzheimers disease provide new diagnostic and therapeutic opportunity to delay or prevent clinical symptoms. It is the most common cause of dementia Alzheimers Association 2020 and the number of its victims continues to expand as the population agesIt has now become the sixth leading cause of death in the United States Alzheimers Association 2020. Recent studies implicate a possible role for proteasome inhibition in neuron degeneration and death that occurs in Alzheimers disease AD.
Impaired function of UPP can be evaluated either by assaying the proteasomes protease activity or the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins. Moreover such treatments are potentially applicable to other neurodegenerative diseases caused by the accumulation of aggregation-prone proteins. Alzheimers disease AD the most common cause of dementia is neuropathologically characterized by accumulation of insoluble fibrous inclusions in the brain in the form of intracellular neurofibrillary tangles and extracellular senile plaques.
Impaired proteasome function in Alzheimers disease.
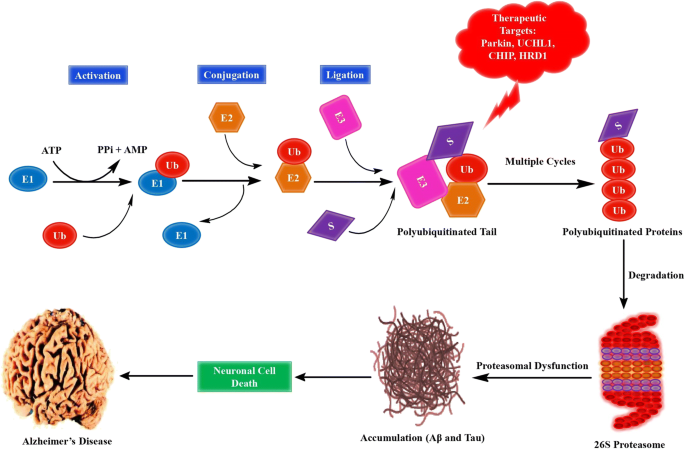
Exploring The Promise Of Targeting Ubiquitin Proteasome System To Combat Alzheimer S Disease Springerlink

Proteins Involved In Ubiquitin Proteasome System Dys Function In Download Table
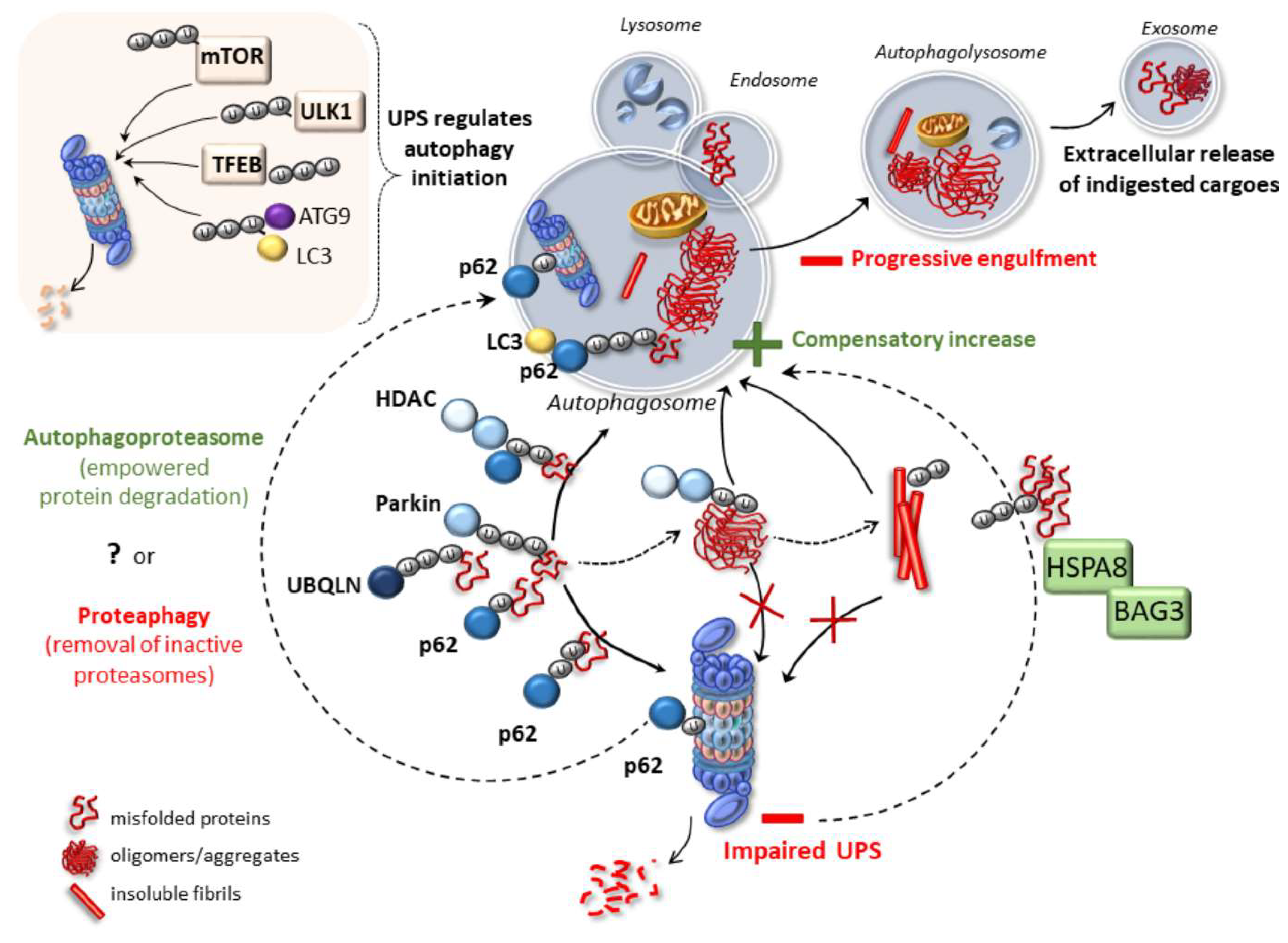
Ijms Free Full Text Promiscuous Roles Of Autophagy And Proteasome In Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies Html

Intracellular Compartment Specific Proteasome Dysfunction In Postmortem Cortex In Schizophrenia Subjects Molecular Psychiatry
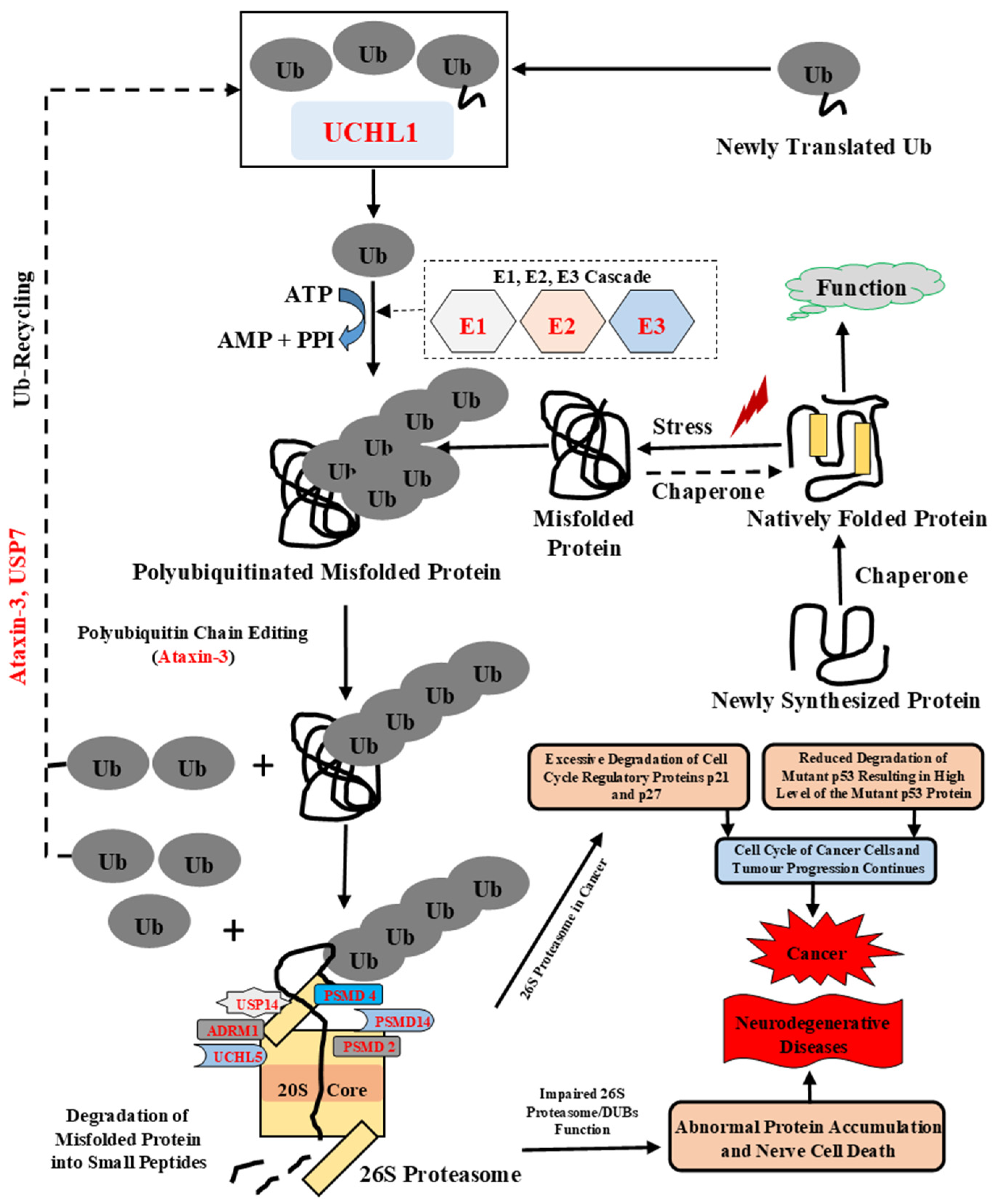
Biomolecules Free Full Text Unstructured Biology Of Proteins From Ubiquitin Proteasome System Roles In Cancer And Neurodegenerative Diseases Html
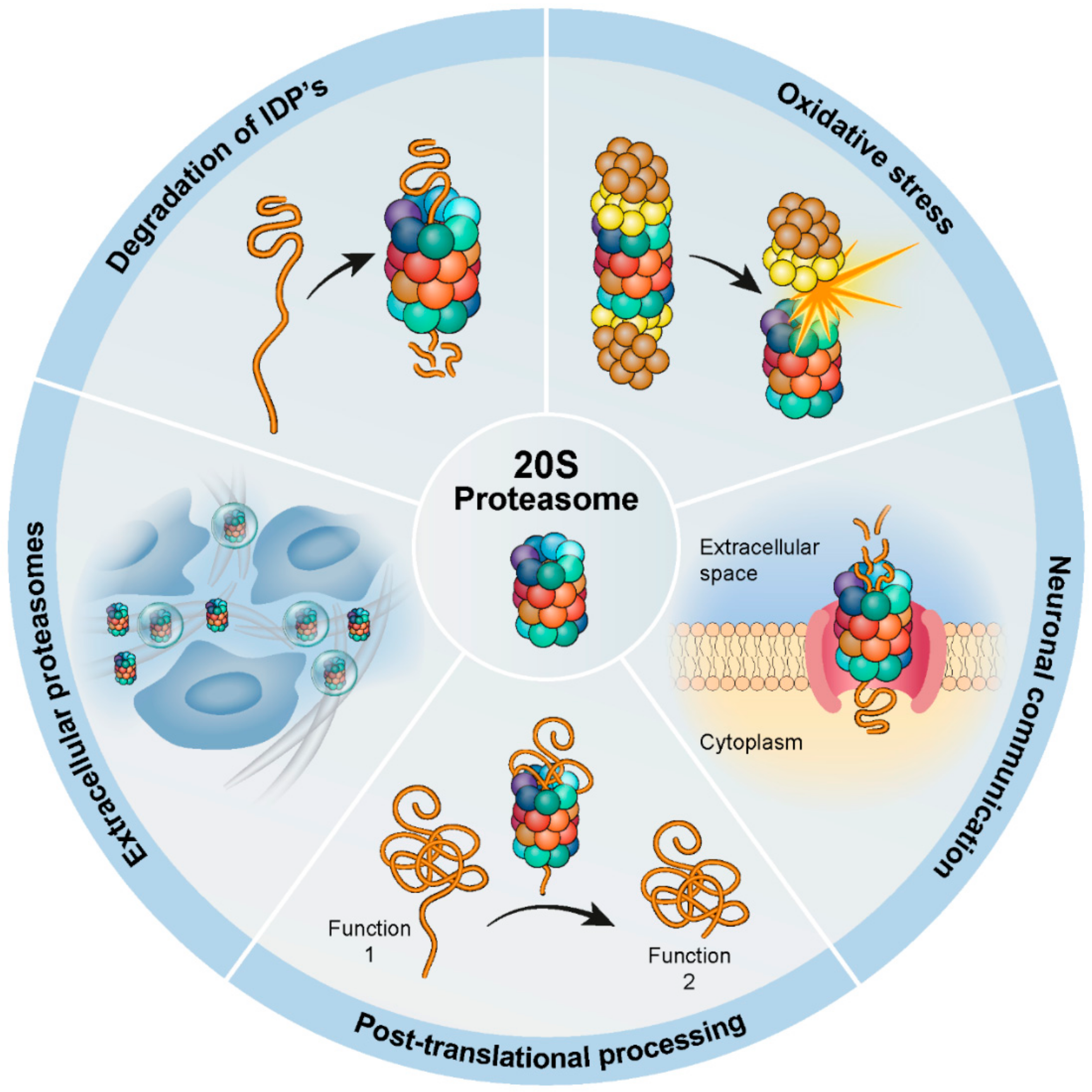
Biomolecules Free Full Text The Contribution Of The 20s Proteasome To Proteostasis Html

The Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway In Health And Disease Of The Nervous System Trends In Neurosciences

Alzheimer S Disease Meets The Ubiquitin Proteasome System Trends In Molecular Medicine

Priming The Proteasome To Protect Against Proteotoxicity Trends In Molecular Medicine
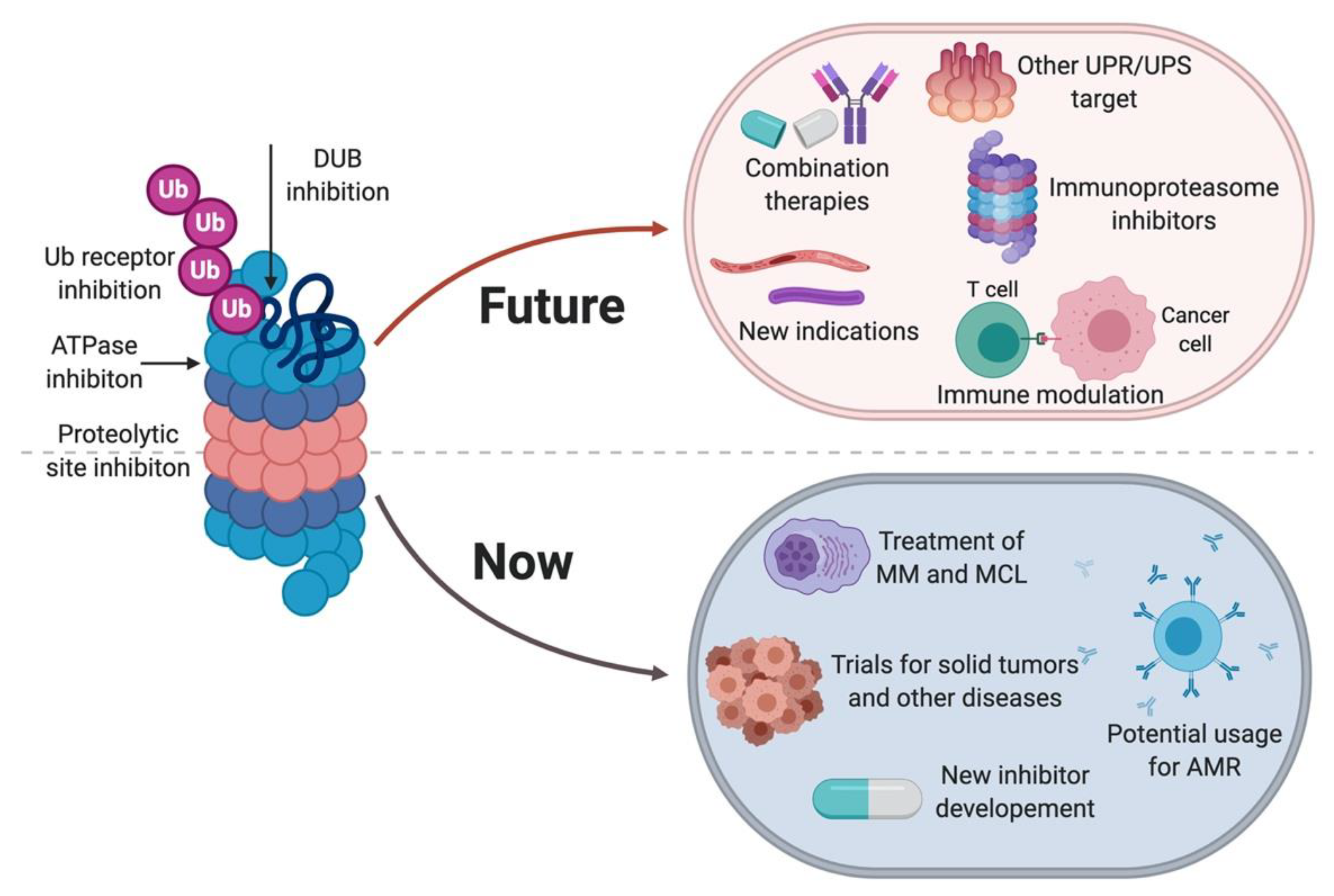
Molecules Free Full Text Proteasome Inhibitors Harnessing Proteostasis To Combat Disease Html

The Proteasome In Alzheimer S Disease And Parkinson S Disease Lessons From Ubiquitin B 1 Trends In Molecular Medicine

The Ubiquitin Proteasome System In The Pathogenesis Of Alzheimer S Download Scientific Diagram

Proteasome And Neurodegenerative Diseases Sciencedirect
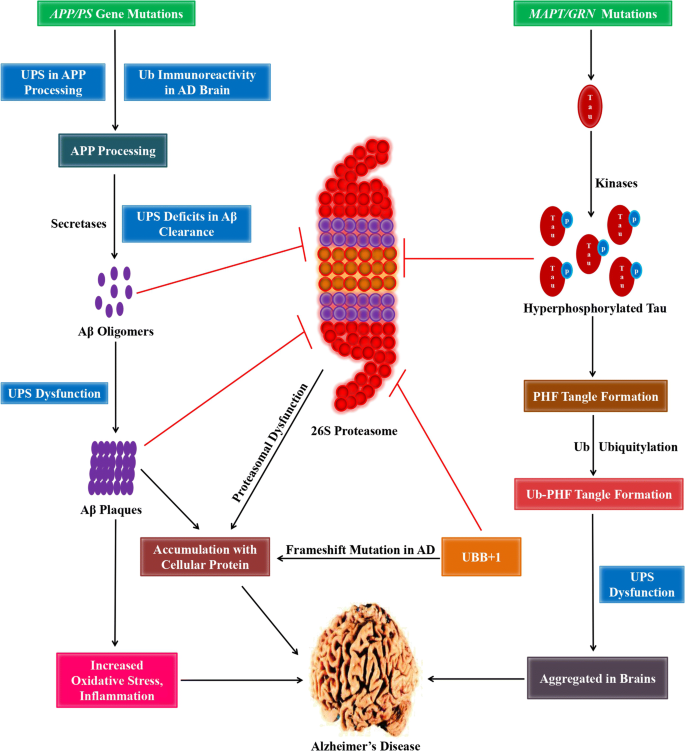
Exploring The Promise Of Targeting Ubiquitin Proteasome System To Combat Alzheimer S Disease Springerlink

The 26s Proteasome Ubiquitinated Proteins Bound To The 19s Are Download Scientific Diagram

A Simplified Representation Of The A Ubiquitin Dependent 26s Download Scientific Diagram

Targeting The 26s Proteasome To Protect Against Proteotoxic Diseases Trends In Molecular Medicine

Lewy Bodies In Parkinson S Disease Lewy Body Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons Disease Nursing
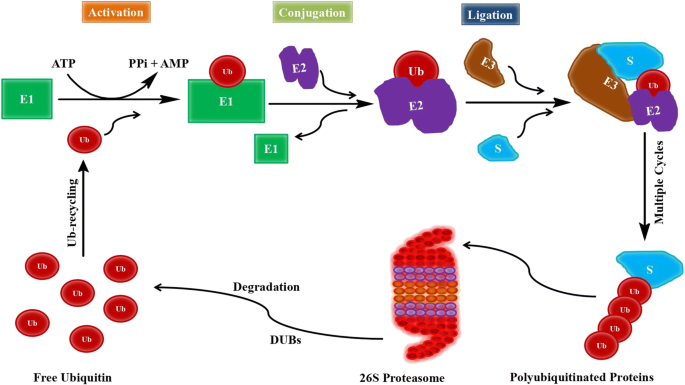
Exploring The Promise Of Targeting Ubiquitin Proteasome System To Combat Alzheimer S Disease Springerlink
0 Response to "Impaired Proteasome Function In Alzheimer’s Disease"
Post a Comment